Pogo Pins for Wire Harness Applications
Pogo Pins are small electrical contact pins with an internal spring mechanism designed to ensure reliable electrical contact. They are one of the most commonly used types of spring connectors, widely adopted across various electronic and industrial applications. Pogo pins play a critical role in the wiring harness industry by providing highly reliable, vibration-resistant electrical connections, especially suited for applications requiring frequent mating cycles and limited space.
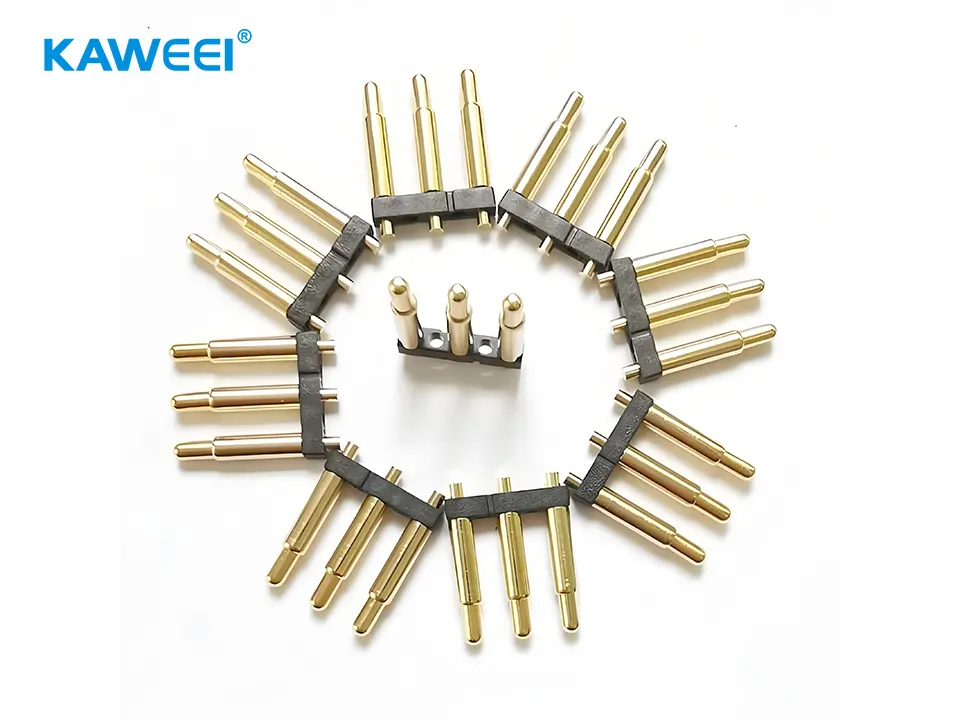

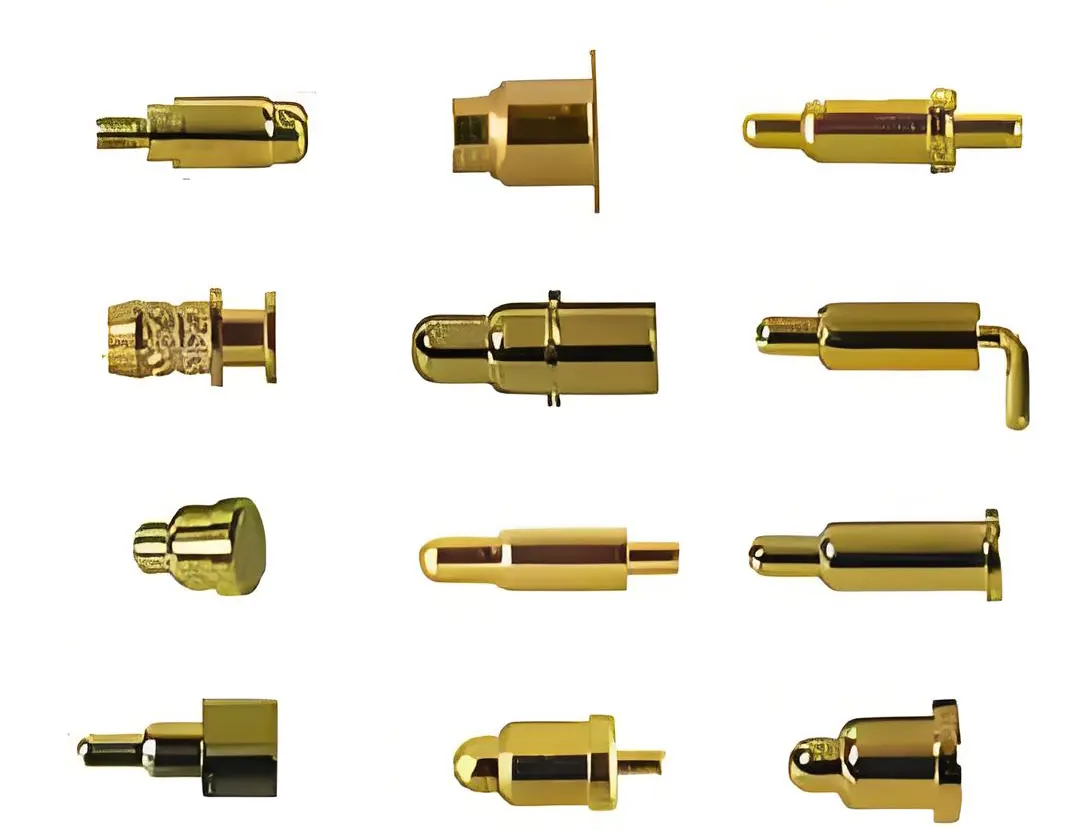
The main components of Pogo Pins include:
- Plunger/Tip: Responsible for contacting the mating surface and conducting current. Typically gold-plated or made from other wear-resistant materials to ensure excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance.
- Spring: Located inside the pin core, it provides stable spring force to maintain consistent and uniform contact pressure against the mating surface, ensuring a reliable connection.
- Barrel/Shell: Encases the plunger and spring, guiding the plunger’s movement and protecting the internal structure, while also serving as part of the electrical contact.
- Tail: Used to connect to PCBs or wiring harnesses, available in various forms such as solder pads, pins, or crimp terminals.
Common types of Pogo Pins:
- Standard Pogo Pins: Suitable for most testing and connection scenarios.
- Long Stroke Pogo Pins: Support larger compression travel, ideal for applications with greater mating tolerances.
- Micro Pogo Pins: Compact size, designed for precision electronics and consumer products.
- Spring Leaf Pogo Pins: Feature a spring leaf design to enhance elasticity and durability.
- High Current Pogo Pins: Designed for high current transmission with specially engineered pin bodies and springs.
Typical applications of Pogo Pins:
- Circuit Board Testing: Used as ICT (In-Circuit Test) probes on smartphone mainboards for rapid electrical testing of chips and circuits. For example, on the Apple iPhone production line, pogo pins test various electrical nodes on the motherboard.
- Charging Interfaces: Serve as wireless charging contact points in smartwatches (e.g., Apple Watch) and wireless earbuds (e.g., AirPods), ensuring stable charging.
- Electronic Module Connections: Provide flexible connections between smartphone camera modules and mainboards, maintaining stable signal transmission while allowing slight movement.
- Automation Equipment: Electrical connections between robot end-effectors and control systems, supporting frequent mating and vibration environments.
- Medical Devices: Connect sensors and main control boards inside wearable heart rate monitors, guaranteeing precise and reliable signals.
pogo pins FAQ:
Q1: What are pogo pins and why are they important in wiring harnesses?
A: Pogo pins are small electrical contact pins with built-in springs that provide reliable, vibration-resistant connections. In wiring harnesses, they ensure stable electrical contact even under frequent plugging and unplugging and in tight spaces.
Q2: What are the main components of a pogo pin?
A: A pogo pin consists of a plunger (tip), spring, barrel (shell), and tail, each designed to ensure consistent contact pressure, durability, and easy connection to PCBs or wiring harnesses.
Q3: What types of pogo pins are commonly used?
A: Common types include standard pogo pins, long stroke, micro, spring leaf, and high current pogo pins, each tailored for specific applications from precision electronics to high current transmission.
Q4: Where are pogo pins typically used?
A: Pogo pins are used in circuit board testing (e.g., smartphone ICT tests), charging interfaces (smartwatches, earbuds), electronic module connections, automation equipment, and medical devices.
Q5: How can Kaweei help with wiring harness solutions involving pogo pins?
A: Kaweei is a professional wiring harness manufacturer offering custom solutions that integrate pogo pins to meet your specific electrical and mechanical requirements, ensuring high reliability and performance.




