What is coaxial cable?
coaxial cable (commonly referred to as Coax) is a type of cable designed for the transmission of high-frequency electrical signals. The term coaxial refers to its construction, where the inner conductor and the outer shielding layer share the same central axis.

It is widely used to transmit high-frequency signals such as television broadcasting, broadband internet, and radio communications.
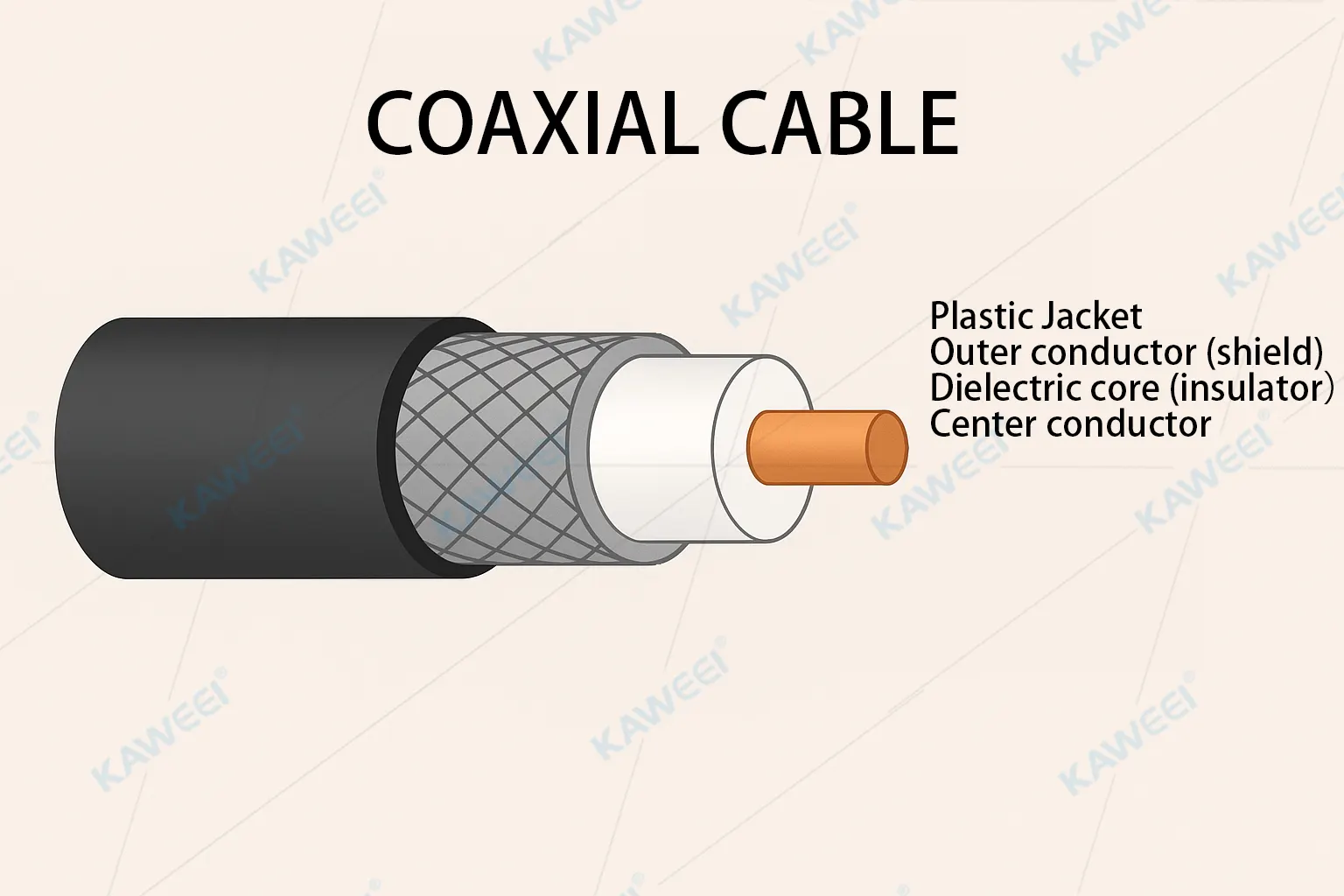
Structure of Coaxial Cable:
- Inner Conductor: Typically made of copper, responsible for carrying the electrical signal.
- Dielectric Insulation: Surrounds the inner conductor, preventing signal leakage.
- Metal Shielding Layer: Usually a braided mesh or metal foil, designed to provide electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding.
- Outer Jacket: The protective outer sheath (usually PVC or other polymers) for mechanical and environmental protection.
Advantages of Coaxial Cable:
- Excellent EMI Immunity: The shielding layer effectively blocks external electromagnetic interference and prevents high-frequency signal leakage.
- High Bandwidth & Transmission Capacity: Supports a wide frequency range, enabling the transmission of high-definition video, internet data, and multi-channel CATV signals.
- Low Signal Attenuation: Compared with twisted pair cables, coaxial cables exhibit lower signal loss at high frequencies, allowing longer transmission distances without amplification.
- Stable Impedance Characteristics: Standard coaxial cables (e.g., 50Ω and 75Ω) maintain consistent characteristic impedance, ensuring impedance matching, minimizing reflection, and preserving signal integrity.
Typical Applications of Coaxial Cable
- Video Transmission: CCTV surveillance systems (commonly RG59, RG6), analog television, CATV distribution, and video conferencing systems.
- Automotive Electronics: In-vehicle cameras (ADAS, 360° surround view, reversing cameras), automotive antennas (GPS, 4G/5G, satellite radio).
- Medical Equipment: Advanced imaging systems such as MRI, CT scanners, and X-ray machines.
- Industrial & Test Equipment: High-speed data transmission in industrial automation, RF/microwave test and measurement setups.
- Military & Aerospace: Communication systems for aircraft and naval vessels, as well as radar and tactical RF systems.

Key Considerations for Custom Coaxial Cable Assemblies:
Application Requirements
- Operating Environment: Indoor/outdoor, high/low temperature tolerance, water/oil/UV resistance.
- Compliance & Certification: RoHS, REACH, UL, automotive-grade (AEC-Q200), medical-grade certifications as required.
Cable Parameters
- Impedance: Typically 50Ω (RF communications, wireless devices) or 75Ω (video, CCTV).
- Shielding Effectiveness: Shielding coverage (braid density, single/double shield) determines EMI immunity.
Connector Requirements
- Interface Type: BNC, SMA, Fakra, MCX, U.FL, N-type, TNC, etc.
- Plating/Material: Gold-plated, nickel-plated — affects durability and cost.
Harness Processing Requirements
- Cable Length: Specified to cm or mm accuracy to ensure proper fit.
- Forming/Assembly: Branching, bundling with cable ties, exposed braid shielding if required.
Kaweei Coaxial Cable FAQ:
Q: What information is needed to customize a coaxial cable?
A: Just provide impedance (50Ω/75Ω), length, connector type, and usage environment.
Q: Where can Kaweei coaxial cables be used?
A: Widely applied in CCTV/video, automotive electronics, industrial testing, medical equipment, and military/aerospace.
Q: Does Kaweei provide testing and certifications?
A: Yes, we offer electrical performance tests, environmental reliability tests, and support RoHS, UL, automotive-grade, and medical-grade certifications.





