What is HDMI?
What is HDMI?
HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface) is a proprietary audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed video data and compressed or uncompressed digital audio data from an HDMI-compliant source device to a compatible display or module.
The HDMI interface supports a maximum data transfer bandwidth of up to 18 Gbps, enabling the transmission of uncompressed audio and high-resolution video signals. Since no digital-to-analog or analog-to-digital conversion is required before signal transmission, it ensures the highest quality of audiovisual signal integrity.
One major advantage of using HDMI is that a single cable can carry both audio and video signals simultaneously, resulting in superior audiovisual transmission quality.
Xuanzhan Technology’s integrated HD and 4K ultra-high-definition core modules commonly employ the HDMI interface. Through Micro HDMI to LVDS conversion, these modules can transmit 1080P HD and 4K UHD audio and video signals.
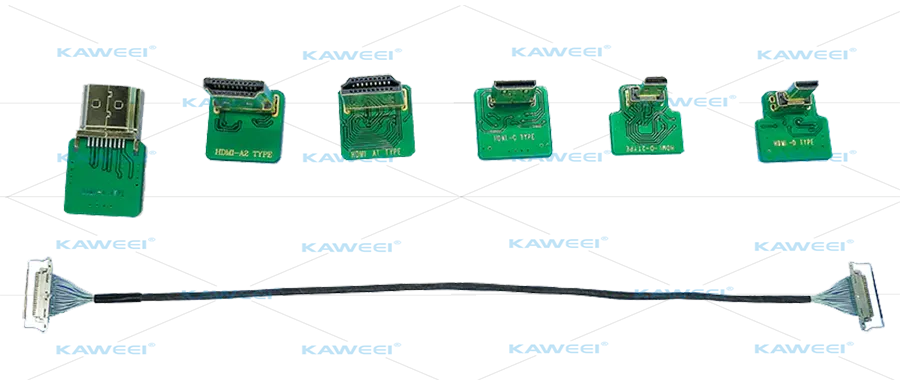
History of HDMI
The HDMI interface was first introduced in December 2002.
The initial version, 1.0, was notable for integrating a digital audio stream interface. Compared to the DVI interface, which was widely used in PCs at the time, HDMI 1.0 supported video streams from DVD up to Blu-ray formats. It enabled universal connectivity among all compatible devices and offered more convenient control over device groups.
From HDMI 1.0 to HDMI 2.0b, the standard underwent nine iterations.
HDMI 2.0 expanded the bandwidth to 18 Gbps, supporting plug-and-play, hot-plugging, 3840×2160 resolution, and frame rates of 50FPS and 60FPS. In addition, it supports up to 32 audio channels and a maximum sampling rate of 1536 kHz.
HDMI 2.0 did not introduce new cable, connector, or interface specifications, ensuring full backward compatibility with HDMI 1.x. Existing Category 2 cables can be used directly.
HDMI 2.0 was not intended to replace HDMI 1.x but rather to enhance it. Any device supporting HDMI 2.0 must first be compatible with the HDMI 1.x standard.
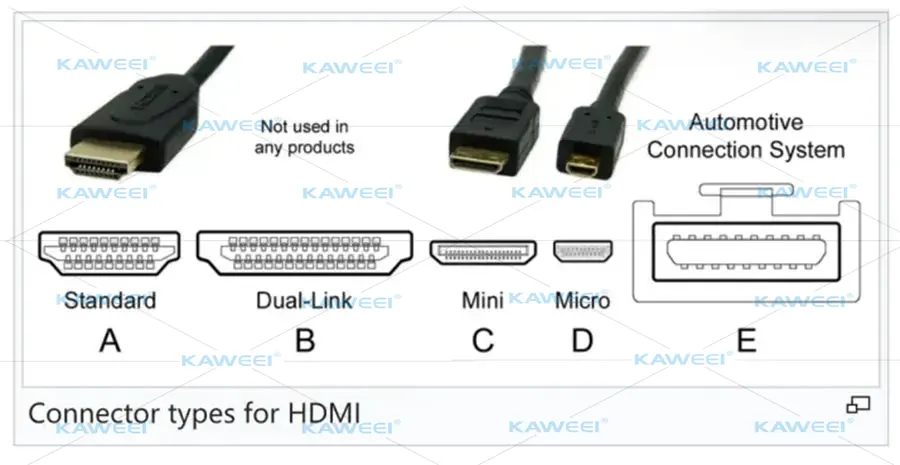
HDMI Connector Types
HDMI connectors are categorized into five types: A, B, C, D, and E.
- Type A is the most common.It is typically found in devices such as flat-panel TVs and core modules. The Type A connector has 19 pins, a width of 13.9 mm, and a thickness of 4.45 mm. Approximately 99% of HDMI-equipped devices use this connector size.
- Type B is extremely rare.It has 29 pins and a width of 21 mm, offering nearly double the bandwidth of Type A. It is considered overkill for consumer applications and is only used in specialized professional settings.
- Type C (Mini HDMI) is designed for compact devices.Measuring 10.42 × 2.4 mm, it is nearly one-third smaller than Type A and has limited application.
- Type D (Micro HDMI) is the newest connector type.It features a further reduced size with a dual-row pin design. Similar in size to a Mini USB connector, it is more suitable for portable and in-vehicle devices.
- Type E is primarily used in automotive audio and video systems.Due to the unstable nature of in-vehicle environments, the HDMI Type E is designed to be shock-resistant, moisture-resistant, high-strength, and tolerant of wide temperature variations. It incorporates a mechanical locking mechanism to ensure connection reliability.
Although HDMI connector types vary, their functionality remains consistent. A quality HDMI connector typically withstands at least 5,000 mating cycles; even with daily use, it can last over 10 years, demonstrating high durability.
It is also worth noting that HDMI is backward compatible with DVI interfaces. Using an HDMI-to-DVI adapter, older DVI devices can be connected. Since DVI also uses TMDS (Transition Minimized Differential Signaling) technology, the video signal can be transmitted seamlessly. However, DVI devices do not support CEC (Consumer Electronics Control) and cannot receive audio signals (grayscale adjustment may be required). Thus, displays with only DVI interfaces can still be connected to HDMI sources.
Key Considerations for Custom HDMI Cable Assemblies:
- Define Bandwidth Requirements: Precisely determine the required HDMI version (e.g., 2.0, 2.1) and cable bandwidth based on video resolution (e.g., 4K@60Hz/120Hz, 8K) and HDR support to ensure lossless signal transmission.
- Connector Selection and Pinout Definition: Strictly adhere to device port types (Standard HDMI, Mini HDMI, Micro HDMI) to define male/female connectors and pin assignments, avoiding physical incompatibility or signal misalignment.
- Cable Specification and Shielding: Select appropriate wire gauge (e.g., AWG26/28) based on transmission distance. For long-distance transmission, prioritize double-layer shielding (foil + braid) to resist electromagnetic interference and maintain signal integrity.
- Connector Technology and Strain Relief: Use gold-plated connectors to reduce impedance. For industrial, automotive, or UAV applications, specify connectors with locking mechanisms or overmolded strain relief to enhance shock and vibration resistance.
- Rigorous Testing and Validation: Post-production tests should include eye diagram analysis, EDID reading, bandwidth stress testing, and mating cycle endurance tests to ensure compliance with HDMI standards and long-term reliability.
You are always welcome to contact us to learn more about customized HDMI cable assemblies. Our team is ready to provide professional solutions tailored to your specific requirements and applications, ensuring reliable connectivity and performance.




